Inside a Startup’s 5-Day Hiring Journey: Lessons from Hyrefast’s AI-Powered Screening
Explore Hyrefast’s 5-day AI-powered hiring journey and learn how startups can speed up screening, reduce bias, and hire top talent faster.
Table of Contents

Introduction
Inside a Startup’s 5-Day Hiring Journey: Lessons from Hyrefast’s AI-Powered Screening
1. Introduction

In the high-stakes world of startups, where runway is tight and every hire can alter the company's trajectory, the traditional recruitment process often feels like a luxury we cannot afford.
On professional networks like LinkedIn, the conversation is saturated with anecdotes of hiring cycles stretching for weeks, consuming precious time and resources that early-stage companies simply do not have. The sentiment is clear: the old way is broken.
This is the problem that Hyrefast, an AI-powered hiring platform, set out to solve-not just for its clients, but for itself.
Faced with the urgent need to scale their own team, they embarked on an ambitious experiment: to condense the entire hiring journey into a mere five days, powered by intelligent automation.
This article deconstructs Hyrefast's 5-day hiring sprint. We will move beyond the surface-level benefits of efficiency to explore the technical architecture and data-driven decision-making that made it possible.
We will examine how AI-powered screening tools were integrated at each stage, from initial application parsing to final interview analysis, and ground the discussion in the fundamental principle of screening-a concept well-studied in other scientific domains for filtering signal from noise.
Our roadmap is straightforward: we will first frame the core problem with traditional hiring, then dive deep into the day-by-day technical workflow, analyse the challenges and trade-offs involved, and finally synthesise the key lessons for other startups and hiring managers looking to build robust, scalable recruitment systems.
2. The Core Problem: Why Traditional Screening Fails at Scale

At its heart, the initial stage of hiring is a screening problem. In fields like physics, screening refers to the phenomenon where a dominant effect (like gravity) suppresses or masks a weaker one in its vicinity, requiring sophisticated methods to detect the subtle signal.
Shao et al. (2019), in their work on creating 'screening maps' of the Universe, detailed a methodology to identify regions where deviations from General Relativity are suppressed.
Similarly, in recruitment, a small number of highly qualified candidates are often obscured by a large volume of unqualified applications.
Manual screening is akin to trying to map the cosmos with the naked eye-it is inefficient, subjective, and prone to missing critical details.
The friction points are well-known to any hiring manager:
- Time Sink: Manually reviewing hundreds of resumes is a colossal drain on a small team's productivity. Hyrefast's own data indicated that manual screening consumed up to 70% of the recruitment team's time before automation.
- Inconsistent Evaluation: Human reviewers bring unconscious biases and varying interpretations of job requirements, leading to an inconsistent candidate scoring system.
- Scalability Wall: A process that works for ten applications breaks down completely when facing a thousand. This inability to scale efficiently can cause startups to miss out on top talent who are quickly snapped up by faster-moving competitors.
The challenge, therefore, is to architect a system that can automatically 'screen' the application field, consistently identifying the high-potential signals amidst the noise, much like the algorithms used to create cosmological screening maps.
3. Deconstructing the 5-Day AI-Powered Workflow
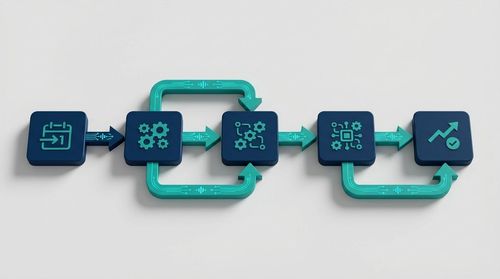
Hyrefast’s approach was not merely about speed; it was about creating a structured, data-centric pipeline where AI augments human decision-making at every step.
Day 1: Strategic Job Description and Intelligent Posting
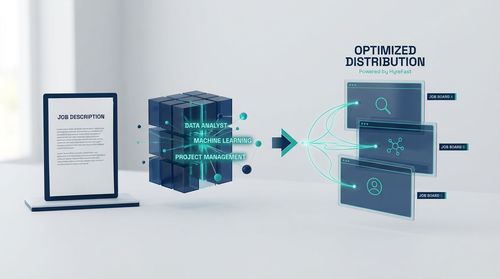
The journey begins with high-quality input. A well-defined job description (JD) is the foundational dataset for the entire AI system.
Hyrefast emphasised crafting JDs that were not just lists of skills but also embedded keywords related to company culture, values, and mission.
This depth of information is crucial for training models to look beyond keyword matching.
The AI's role here was in distribution optimisation-analysing which job boards and channels had historically yielded the highest-quality candidates for similar roles, ensuring the JD reached the most relevant audience from the start.
Day 2: AI-Powered Application Screening and Ranking
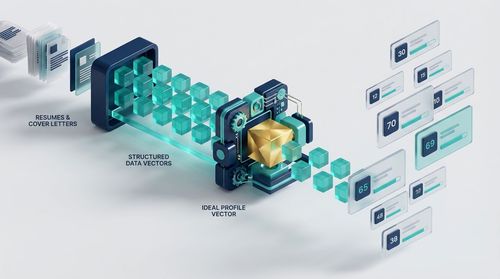
This is where the core screening mechanism comes into play. Instead of a simple keyword scanner, the system likely employed Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques to parse resumes and cover letters.
The goal is semantic understanding: differentiating between a candidate who "used Python" on a university project and one who "architected and deployed a Python-based microservices platform."
Each application is converted into a structured data vector, encompassing skills, experience duration, project complexity, and achievement metrics.
A scoring algorithm then ranks candidates against the ideal profile vector derived from the JD.
This process mirrors the Monte Carlo simulations used in scientific screening, such as in the work of Loth and Shklovskii (2009) on ion screening, where numerous probabilistic interactions are modelled to find a stable configuration.
Here, the algorithm models the candidate's fit probabilistically, providing a quantifiable, bias-mitigated score that prioritises applicants for human review.
This step alone accounted for Hyrefast's reported 70% reduction in manual screening time.
Day 3: Video Interviews with Integrated Analysis

The top-ranked candidates proceed to a video interview. The AI's role evolves from static analysis to dynamic assessment. Modern platforms can analyse video content for more than just words.
Through audio and video processing, they can provide meta-insights on communication clarity, sentiment, and even non-verbal cues (though this area requires careful ethical consideration to avoid new forms of bias).
The primary utility is in transcribing the interview and flagging key moments where candidates demonstrated core competencies, allowing reviewers to quickly navigate to the most relevant parts of the conversation.
Day 4: Simulated Skills Assessment

For technical roles, a practical assessment is non-negotiable. Hyrefast used AI to generate or curate skills tests that simulated real-world problems. The advantage here is consistency and scalability.
Every candidate faces the same challenges under comparable conditions.
The AI can assist in initial scoring of code-based tasks (e.g., testing for functionality, efficiency, and cleanliness) or provide a detailed performance breakdown, highlighting strengths and areas for concern before the final human evaluation.
Day 5: Synthesised Decision-Making and Offer

By the final day, the hiring team is not acting on gut feeling alone. They are equipped with a comprehensive data packet for each shortlisted candidate: the initial application score, video interview insights, and detailed skills assessment results.
This triangulation of data points enables a more informed and confident final interview. The discussion shifts from "What did we think?" to "What does the data show?"
This synthesis of AI-derived evidence and human judgment on cultural fit culminates in a rapid offer process, often automated through the platform.
4. Navigating the Challenges and Trade-Offs

Implementing such a system is not without its challenges. The promise of AI screening is often met with valid concerns.
- Algorithmic Bias: If the training data for the screening models is biased, the system will perpetuate and potentially amplify those biases. The mitigation lies in continuous auditing of the algorithms for fairness across gender, ethnicity, and educational background. Hyrefast's claim of bias elimination is an ongoing pursuit, not a one-time achievement.
- The Black Box Problem: Over-reliance on a scoring algorithm without understanding its reasoning can be dangerous. The trade-off between a complex, high-performing model and a simpler, interpretable one is critical. Startups must ensure their tools provide explainable AI features, showing why a candidate was scored a certain way.
- Cost vs. Control: While AI tools save significant personnel time, they represent a direct financial cost. For a very early-stage startup hiring for one or two roles, a full-suite platform might be overkill. The decision rule is straightforward: when the volume of applications and the opportunity cost of time exceed the subscription cost, the investment becomes justified.
5. Conclusion and Lessons Learned
Hyrefast's 5-day journey is a compelling case study in applying a systematic, AI-augmented approach to a traditionally chaotic process. The lessons extend beyond mere speed.
- Screening as a Technical Discipline: Treating candidate screening as a serious data filtering problem, akin to methodologies in other sciences, forces rigour and consistency into the process.
- AI as an Augmenting Tool, Not a Replacement: The greatest success came from using AI to handle high-volume, repetitive tasks (scanning resumes, scheduling, transcribing) and providing data-driven insights, leaving the nuanced final decisions to humans.
- Data Integrity is Paramount: The entire system's quality depends on the quality of the initial input-the job description. A vague JD will lead to a poorly trained model and unreliable results.
- Efficiency Gains are Transformational: Reclaiming 70% of a hiring manager's time translates directly into increased productivity in other critical business areas, creating a compound positive effect on startup growth.
6. Future Directions

The evolution of AI in hiring is just beginning. Based on current trends, we can anticipate several developments:
- Advanced Explainability (XAI): Future tools will provide even clearer rationales for their scores, building greater trust and facilitating smoother human-in-the-loop workflows.
- Predictive Performance Analytics: Models will evolve from assessing current fit to predicting a candidate's long-term success and growth potential within a specific company culture.
- Integration with Continuous Learning: Recruitment platforms will likely integrate with internal performance data, creating a feedback loop that continuously refines the screening algorithms based on which hires actually succeeded.
- Ethical AI Frameworks: As scrutiny increases, we will see the emergence of standardised, auditable frameworks for ensuring fairness and transparency in AI-powered hiring tools.
Hyrefast’s experiment demonstrates that with the right architectural mindset, startups can turn hiring from a draining bottleneck into a strategic, scalable advantage.
7. References
- LinkedIn Article on Hyrefast's Hiring Journey: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/inside-startups-5-day-hiring-journey-lessons-hyrefasts-ai-screening/
- Shao, L. et al. (2019) "Screening maps of the local Universe I -- Methodology." ArXiv. (For the conceptual framework of screening methodologies).
- Loth, M. S. & Shklovskii, B. I. (2009) "Non-mean-field screening by multivalent counterions." ArXiv. (For insights into probabilistic screening models).
