Top 7 AI Hiring Tools Every Indian Startup Should Know in 2025
Top 7 AI hiring tools for Indian startups in 2025. Compare HireVue, HackerRank, Pymetrics & more to hire faster, reduce bias, and scale smartly.
Table of Contents

Introduction
For an Indian startup, every hire is critical. In the competitive landscape of 2025, where speed, cost-efficiency, and finding the right talent are paramount, traditional hiring methods are becoming a bottleneck.
The conversation on professional networks like LinkedIn is rife with debates:
Can AI truly understand the nuances of a startup's culture?
Can it help us move faster without compromising on quality? The answer, increasingly, is a qualified yes.
Artificial Intelligence is no longer a futuristic concept; it's a practical toolkit that is reshaping recruitment from a reactive process into a strategic, data-driven function.
This article is not about a distant future. It's a practical guide for founders and hiring managers in Bengaluru, Hyderabad, and Pune who are grappling with scaling their teams effectively.
We will dissect seven powerful AI hiring tools that have proven their value in the market. We'll move beyond the hype to understand what each tool does, the specific startup problem it solves, and the technical considerations you must weigh before adoption.
In a resource-constrained environment, making an informed choice can be the difference between building a stellar team and wasting precious time and capital.
1. HireVue: Automating the First Impression with AI-Powered Video Interviews

HireVue is an AI-powered video interviewing platform that addresses one of the most time-consuming phases of hiring: the initial screening.
For a startup inundated with applications, scheduling and conducting first-round interviews is a massive operational drain. HireVue automates this by allowing candidates to complete video interviews on their own time, answering pre-set questions.
The platform’s AI uses machine learning algorithms and natural language processing (NLP) to analyze candidate responses.
It goes beyond mere transcription, assessing verbal cues, and in some versions, non-verbal cues like facial expressions, to provide insights into communication skills, problem-solving approach, and cultural fit.
This provides hiring managers with structured, data-rich summaries, enabling better decision-making before committing to a live interview.
- Indian Startup Fit: Excellent for startups looking to efficiently filter a high volume of applicants, especially for roles where communication is key. It also democratizes access by allowing candidates from any location to participate.
- Consideration: The use of facial analysis technology is a subject of ethical debate. Startups must critically evaluate the potential for algorithmic bias and ensure the tool aligns with their diversity and inclusion goals.
2. Pymetrics: Assessing Potential with Neuroscience-Based Games
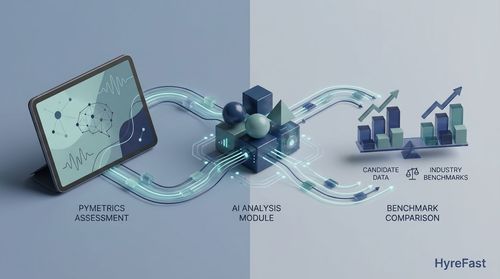
Pymetrics tackles the problem of resume-based bias by focusing on potential rather than pedigree. It uses AI to assess a candidate's cognitive abilities and personality traits through a series of quick, engaging online games.
These games are designed by neuroscientists to measure attributes like risk-taking, attention, memory, and emotional intelligence.
The AI then compares a candidate’s results against a baseline of top performers within your company (or a general benchmark), providing a objective data point on cultural and cognitive fit.
This helps startups uncover hidden talent who might not have a "perfect" resume but possess the intrinsic qualities needed to thrive in a dynamic environment.
- Indian Startup Fit: Ideal for roles where problem-solving, adaptability, and learning agility are more important than specific, prior experience. It’s a powerful tool for building diverse teams and reducing unconscious bias.
- Consideration: The effectiveness of Pymetrics hinges on the quality of the baseline data. For an early-stage startup without an established team, relying on general benchmarks may be necessary.
3. HackerRank: Objectively Gauging Technical Skills at Scale
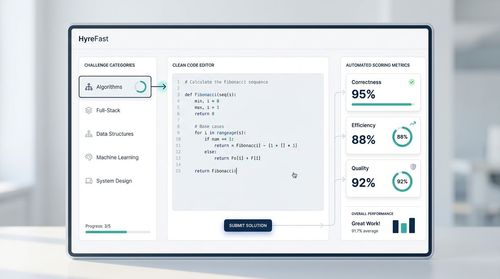
For tech startups, accurately assessing coding skills is non-negotiable. HackerRank provides an AI-powered platform that offers a vast library of real-world coding challenges and projects.
Candidates can be tested on everything from fundamental algorithms to full-stack development in a standardized environment.
The AI component automates code review, evaluating submissions for correctness, efficiency, and quality.
It provides detailed reports on a candidate’s problem-solving approach and technical proficiency.
Beyond hard skills, HackerRank also offers assessments for soft skills like communication and collaboration, providing a more holistic view.
- Indian Startup Fit: A must-consider tool for any Indian startup hiring engineers. It streamlines technical screening, ensures a consistent evaluation standard, and provides concrete data to compare candidates objectively.
- Consideration: While excellent for evaluating technical ability, it should be one part of a broader hiring process that includes interviews to assess system design and cultural alignment.
4. Entelo: Proactive Sourcing with Predictive Analytics
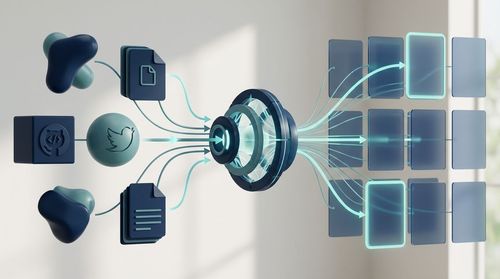
Finding candidates, not just reviewing applications, is a major challenge. Entelo is an AI-driven sourcing and engagement platform that uses predictive analytics to identify potential candidates who may not be actively job hunting.
It scans millions of public data points from across the web (like GitHub, Twitter, and professional blogs) to build rich candidate profiles.
The AI algorithms analyze this data to predict candidates who are most likely to be open to new opportunities and are a strong fit for your specific role requirements. This allows startups to proactively build a talent pipeline, a crucial advantage in a competitive market.
- Indian Startup Fit: Perfect for startups looking to hire for niche or senior roles where the best talent is often already employed and not browsing job portals.
- Consideration: The quality of sourcing depends on the algorithm's training data. It's essential to fine-tune search parameters to avoid generic results and ensure you're reaching the right talent pool.
5. Gloat: Unlocking Internal Talent Mobility and Referrals
Gloat functions as an internal talent marketplace, using AI to match employees with internal projects, mentorship opportunities, and even new roles within the startup.
For a growing company, retaining good talent is as important as hiring new ones. Gloat helps by providing employees with visibility into internal growth paths, increasing engagement and retention.
Additionally, some data sources position Gloat as a referral marketing platform.
In this context, its AI would identify top performers within a company's network and incentivize effective referrals, leveraging the most reliable source of quality hires: employee networks.
- Indian Startup Fit: Highly valuable for startups that are scaling rapidly and need to manage internal mobility effectively, preventing silos and retaining institutional knowledge.
- Consideration: This tool becomes more relevant as a startup grows beyond its founding team (e.g., 50+ employees), when structured internal mobility becomes a strategic priority.
6. InterviewBit & CodinGame: Specialised Platforms for Developer Hiring
InterviewBit and CodinGame are highly specialised tools that cater specifically to the developer hiring ecosystem.
- InterviewBit is not just an assessment tool but also an interview preparation platform for candidates. For startups, this dual nature is beneficial. The platform provides tools for hiring managers to conduct structured technical interviews with a curated set of problems and real-time code collaboration features. This brings consistency and depth to the final interview stage.
- CodinGame takes a unique approach by turning coding assessments into interactive games. This gamified experience can be more engaging for candidates and can attract a different segment of developers who enjoy solving puzzles and challenges. The AI evaluates the code and problem-solving strategy in real-time.
- Indian Startup Fit: Both are excellent complements to HackerRank. InterviewBit is strong on structured interviews, while CodinGame is great for attracting and assessing developers in a more engaging format.
- Trade-off: The gamified approach of CodinGame, while engaging, may need to be supplemented with more traditional coding tests to assess candidates for specific, practical job tasks.
7. ZipRecruiter: AI-Driven Job Distribution and Matching
ZipRecruiter is a powerful AI-powered recruitment platform that excels at distribution and matching.
Startups post a job, and ZipRecruiter’s AI actively promotes it across hundreds of job boards and uses matching technology to recommend the job to suitable candidates and candidates to the company.
It provides real-time data on candidate engagement (e.g., how many views and applications your post receives) and automated outreach tools to communicate with applicants. This is particularly useful for high-volume hiring needs, such as sales or entry-level operational roles.
- Indian Startup Fit: Best suited for startups that need to fill roles quickly and cast a wide net to attract a large number of applicants.
- Consideration: The broad-reach approach may result in a higher volume of unqualified applicants, so robust screening tools (like those mentioned above) become essential to manage the influx.
Key Considerations for Implementation

Adopting any AI tool requires diligence.
- Bias Mitigation: Tools like DeBiasMe highlight a critical industry focus: mitigating algorithmic bias. Always ask vendors about their debiasing strategies and the diversity of their training data.
- Data Privacy: Be transparent with candidates about how their data is used, especially with tools analyzing video or game-based assessments. Compliance with evolving Indian data protection norms is crucial.
- Human-in-the-Loop: AI is an aid, not a replacement. The final hiring decision should always involve human judgment to assess nuance, empathy, and true cultural fit-qualities AI is still learning to gauge.
Conclusion
The AI hiring landscape in 2025 offers Indian startups an unprecedented opportunity to optimise their most critical function: building a team.
The tools we've explored-from HireVue's efficient screenings to HackerRank's technical rigour and Entelo's proactive sourcing-provide a toolkit to be faster, fairer, and more strategic.
- The key takeaway is to align the tool with your specific pain point: volume screening, technical assessment, or proactive sourcing.
- The strategic imperative is to use these tools to augment human judgment, not replace it, ensuring that the soul of your startup culture is preserved.
- The ethical responsibility lies with the startup to choose transparent, accountable AI that minimizes bias and respects candidate privacy.
By thoughtfully integrating these AI solutions, Indian startups can transform hiring from a daunting challenge into a competitive advantage, paving the way for sustainable growth and innovation.
References
- HireVue Official Website: How HireVue's AI-Powered Platform Works
- Pymetrics Resource Center: Neuroscience and AI in Hiring
- HackerRank Blog: Best Practices for Technical Recruiting
- Entelo Blog: Using Predictive Analytics in Talent Sourcing
- Research on AI Bias in Hiring: ArXiv Paper on Debiasing Algorithms (Representative of tools like DeBiasMe)
- ZipRecruiter Employer Guide: AI Matching Technology
